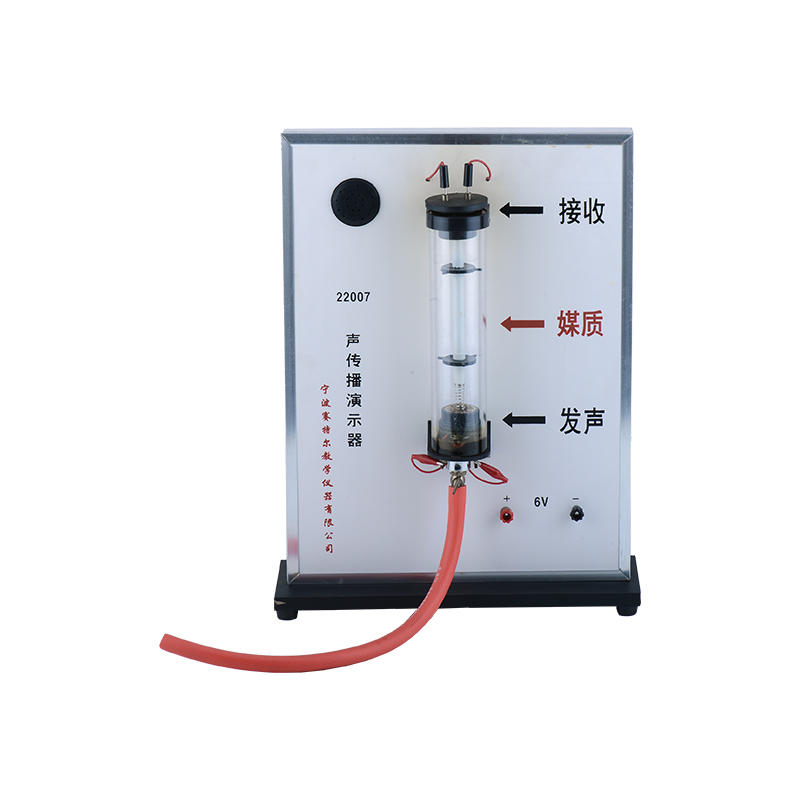
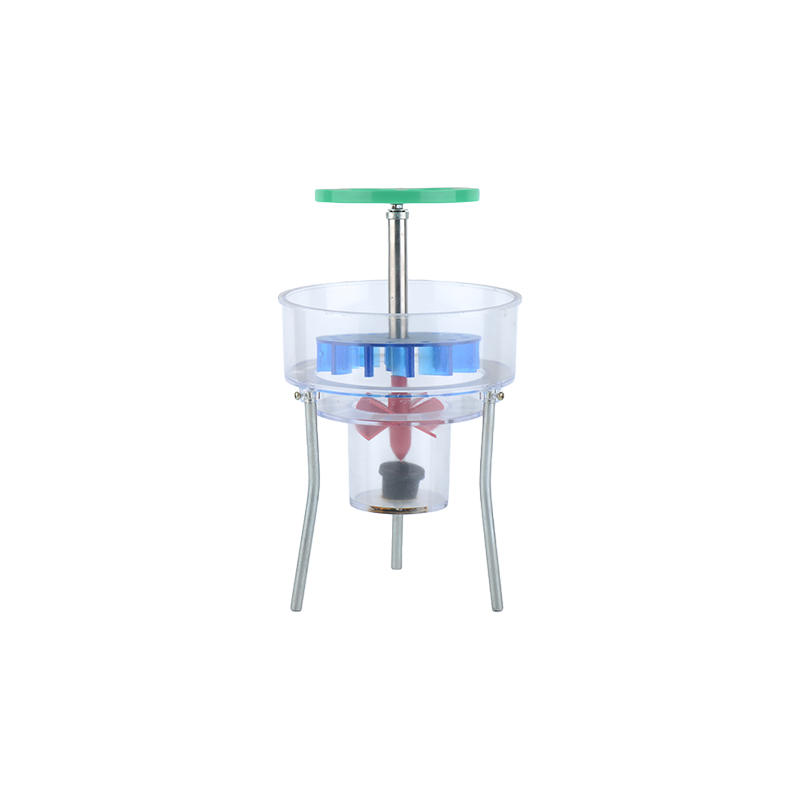
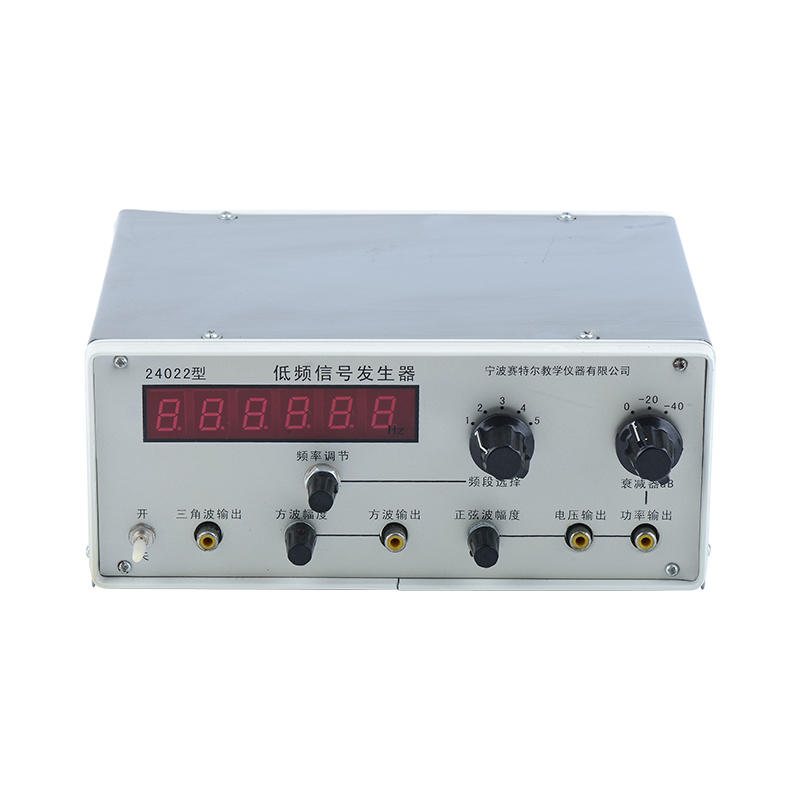
Primary mathematics teaching instrument Description:
Primary mathematics teaching instruments are tools and materials that are used to teach mathematics to young students in primary school. These instruments can include a wide range of materials, such as worksheets, manipulatives, and technology tools.
Worksheets are another type of primary mathematics teaching instrument that can be used to help students practice and reinforce their understanding of mathematical concepts. These can include things like practice problems, word problems, and other activities that help students to apply what they have learned. Worksheets can be used to provide additional practice and support for students who are struggling with a particular concept, or to challenge and extend the learning of more advanced students.
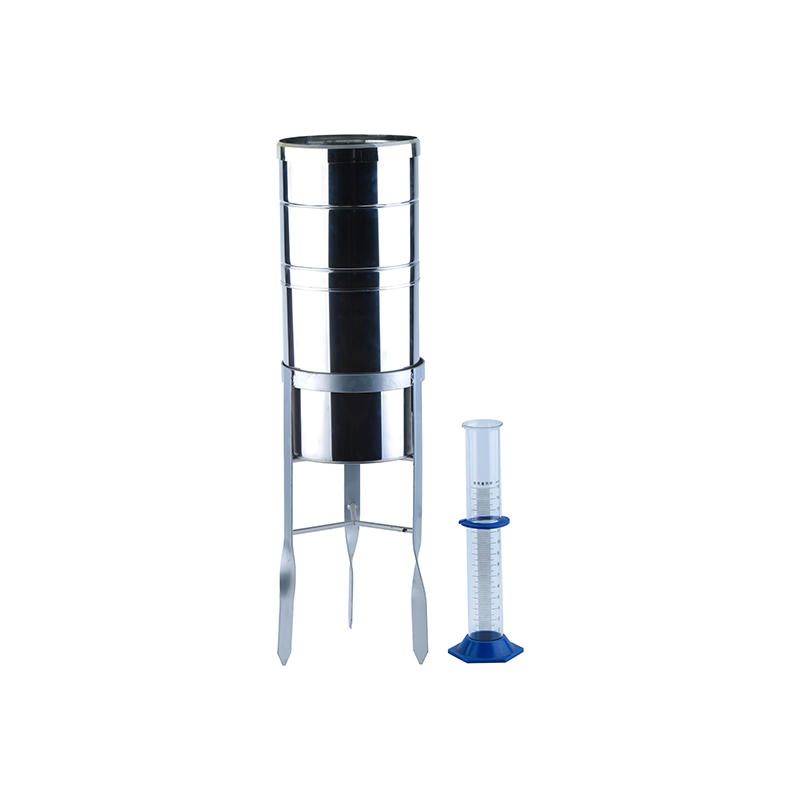
technology tools—rain gauge:use a rain gauge as a teaching tool, you can set it up in an open area outside of the classroom, such as a school lawn or field. The students can then be tasked with checking the gauge regularly and recording the amount of precipitation that has accumulated in the container. This data can be used to help students understand the factors that influence precipitation, such as temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure.
In addition to collecting and recording precipitation data, a rain gauge can also be used to engage students in hands-on activities and experiments related to weather and the water cycle. For example, students could use the data collected from the rain gauge to create graphs or charts that illustrate the amount of precipitation that falls over a given period of time. They could also use the data to make predictions about future weather patterns or to design and conduct experiments related to the water cycle.Overall, a rain gauge can be a useful and engaging teaching tool for helping students learn about weather and the water cycle.
Uses Of Primary mathematics teaching instrument:
Primary mathematics teaching instruments are used to facilitate learning in the primary school math classroom by providing students with the tools and materials they need to understand and master new mathematical concepts and ideas. Some specific uses of primary mathematics teaching instruments include:
Providing students with information: instructional materials can be used to provide students with detailed information on a particular mathematical concept or topic. These materials can be used to introduce new concepts, provide examples and explanations, and provide practice opportunities.
Engaging students visually: Visual aids, such as charts, diagrams, and images, can be useful for helping students understand complex mathematical concepts or ideas. These materials can be used to make abstract ideas more concrete, and can be especially helpful for visual learners.
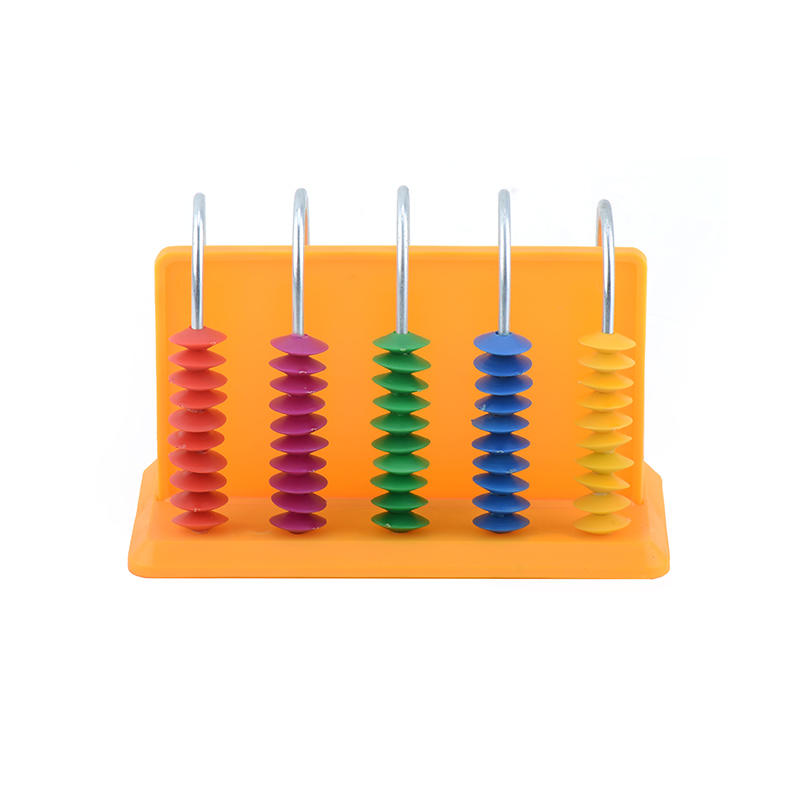
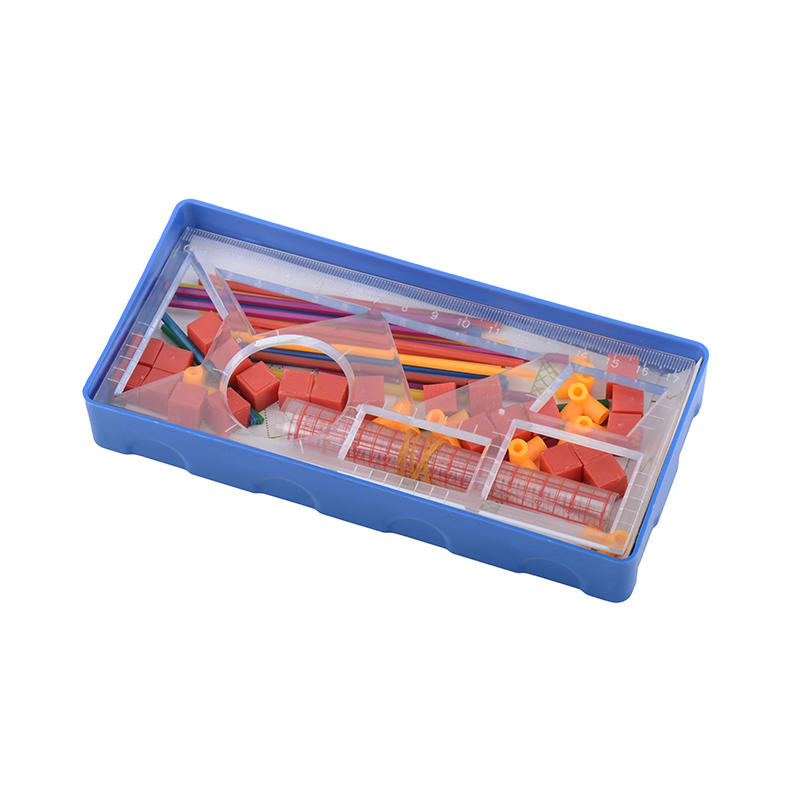
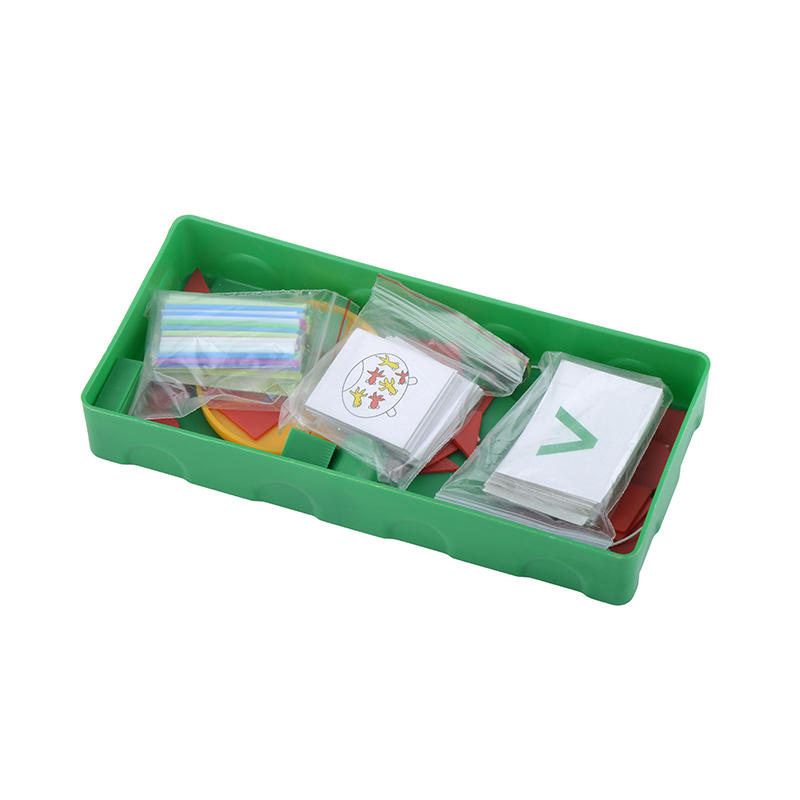
Encouraging hands-on learning: Hands-on materials, such as manipulatives and experiments, can be useful for providing students with a more interactive and engaging learning experience. These materials can help students to apply what they have learned in a more tangible way.
Primary mathematics teaching instrument Production Process:
The production process for primary mathematics teaching instruments will depend on the specific type of instrument being produced. Some general steps that may be involved in the production of primary mathematics teaching instruments include:
Design: The first step in the production process is to design the instrument. This may involve creating drawings or prototypes of the instrument, as well as determining the materials and components that will be used in its construction.
Assembly: Once the materials and components have been procured, the next step is to assemble the instrument. This may involve assembling the components by hand, or using automated machinery to help with the assembly process.
Testing: Once the instrument has been assembled, it is typically tested to ensure that it meets the required standards and specifications. This may involve conducting functional tests to ensure that the instrument is working correctly, or subjecting the instrument to various stress tests to ensure that it is durable and reliable.
Packaging and distribution: Once the instrument has been tested and deemed ready for sale, the next step is to package it and prepare it for distribution. This may involve placing the instrument in boxes or other packaging materials, and arranging for it to be shipped to the final destination.



 中文简体
中文简体 English
English